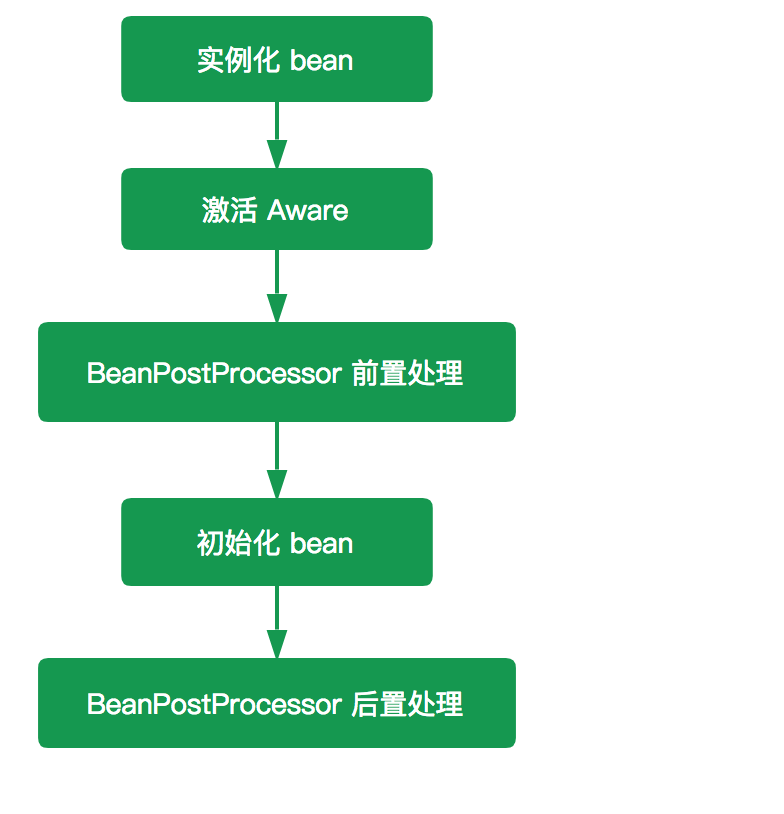
IOC之BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor接口除了Aware这个扩展点,还有BeanPostProcessor,BeanPostProcessor 的作用:在 Bean 完成实例化后,如果我们需要对其进行一些配置、增加一些自己的处理逻辑,那么请使用 BeanPostProcessor。
BeanPostProcessor实例1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class TestBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {"Bean[" + beanName + "]开始初始化" );return bean;@Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {"Bean[" + beanName + "]完成初始化" );return bean;public void display () {"Hello BeanPostProcessor..." );
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd" > <bean id ="testBeanPostProcessor" class ="com.jievhaha.TestBeanPostProcessor" /> </beans >
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public class MyApplication {public static void main (String[] args) {ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource ("applicationContext.xml" );DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory ();XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader (factory);TestBeanPostProcessor testBeanPostProcessor = (TestBeanPostProcessor) factory.getBean("testBeanPostProcessor" );
输出结果为:
1 Hello BeanPostProcessor...
并没有执行前置、后置处理器。
在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean()中:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 protected Object initializeBean (String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {if (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) { return null ;else {Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {try {catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException (null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null ),"Invocation of init method failed" , ex);if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {return wrappedBean;@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null ) {return result;return result;
1 2 3 4 5 6 public List<BeanPostProcessor> getBeanPostProcessors () {return this .beanPostProcessors;private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new BeanPostProcessorCacheAwareList ();
断点中可以查看到getBeanPostProcessors()的size为0。
所以要想执行前置处理器就要保证该List不为空,那就要有this.beanPostProcessors.add()的过程:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @Override public void addBeanPostProcessor (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) {"BeanPostProcessor must not be null" );this .beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor);this .beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor);
该方法是由 AbstractBeanFactory 的父类 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory 接口定义,它的核心意思就是将指定 BeanPostProcessor 注册到该 BeanFactory 创建的 bean 中,同时它是按照插入的顺序进行注册的 ,完全忽略 Ordered 接口所表达任何排序语义(在 BeanPostProcessor 中我们提供一个 Ordered 顺序)。
所以要可以执行前后置处理器,只需增加如下步骤:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 TestBeanPostProcessor test = new TestBeanPostProcessor ();ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource ("applicationContext.xml" );DefaultListableBeanFactory factory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory ();XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader (factory);TestBeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = new TestBeanPostProcessor ();TestBeanPostProcessor testBeanPostProcessor = (TestBeanPostProcessor) factory.getBean("testBeanPostProcessor" );
这样,使用该factory创建任何Bean都会执行前后置处理器,ApplicationContext方法不需手动注册,会自动检测所有BeanPostProcessor然后进行自动注册(都已测试)。
总结:一般普通的 BeanFactory 是不支持自动注册 BeanPostProcessor 的,需要我们手动调用 addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) 方法进行注册。注册后的 BeanPostProcessor 适用于所有该 BeanFactory 创建的 bean,但是 ApplicationContext 可以在其 bean 定义中自动检测所有的 BeanPostProcessor 并自动完成注册,同时将他们应用到随后创建的任何 Bean 中 。
BeanPostProcessor基本原理BeanPostProcessor接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public interface BeanPostProcessor {@Nullable default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;@Nullable default Object postProcessAfterInitialization (Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {return bean;
BeanPostProcessor 可以理解为是 Spring 的一个工厂钩子(其实 Spring 提供一系列的钩子,如 Aware 、InitializingBean、DisposableBean),它是 Spring 提供的对象实例化阶段强有力的扩展点,允许 Spring 在实例化 bean 阶段对其进行定制化修改,比较常见的使用场景是处理标记接口实现类或者为当前对象提供代理实现(例如 AOP)。
postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 和 postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) 两个方法,都接收一个 Object 类型的 bean ,一个 String 类型的 beanName ,其中 bean 是已经实例化了的 instanceBean ,能拿到这个你是不是可以对它为所欲为了? 这两个方法是初始化 bean 的前后置处理器,他们应用 invokeInitMethods(String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) 方法的前后。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 protected Object initializeBean (String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {if (System.getSecurityManager() != null ) { return null ;else {Object wrappedBean = bean;if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {try {catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException (null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null ),"Invocation of init method failed" , ex);if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {return wrappedBean;@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null ) {return result;return result;@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization (Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {Object result = existingBean;for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);if (current == null ) {return result;return result;
自动检测并注册 getBeanPostProcessors() 方法,返回的是 beanPostProcessors 集合,该集合里面存放就是我们自定义的 BeanPostProcessor ,如果该集合中存在元素则调用相应的方法,否则就直接返回 bean 了。这也是为什么使用 BeanFactory 容器是无法输出自定义 BeanPostProcessor 里面的内容,因为在 BeanFactory.getBean(...) 方法的过程中根本就没有将我们自定义的 BeanPostProcessor 注入进来,所以要想 BeanFactory 容器 的 BeanPostProcessor 生效我们必须手动调用 addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) 方法,将定义的 BeanPostProcessor 注册到相应的 BeanFactory 中。但是 ApplicationContext 不需要手动,因为 ApplicationContext 会自动检测并完成注册 。
ApplicationContext 实现自动注册的原因,在于我们构造一个 ApplicationContext 实例对象的时候会调用 AbstractApplicationContext.registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 方法,将检测到的 BeanPostProcessor 注入到 ApplicationContext 容器中,同时应用到该容器创建的 bean 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 protected void registerBeanPostProcessors (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {this );public static void registerBeanPostProcessors (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {true , false );int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;new BeanPostProcessorChecker (beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();new ArrayList <>();for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {else {new ArrayList <>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {new ArrayList <>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {new ApplicationListenerDetector (applicationContext));
逻辑:
首先 beanFactory 获取注册到该 BeanFactory 中所有 BeanPostProcessor 类型的 beanName 数组,其实就是找所有实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口的 bean ,然后迭代这些 bean ,将其按照 PriorityOrdered、Ordered、无序的顺序,添加至相应的 List 集合中,最后依次调用 sortPostProcessors(List postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) 方法来进行排序处理、 registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List postProcessors) 方法来完成注册。
排序 很简单,如果 beanFactory 为 DefaultListableBeanFactory ,则返回 BeanFactory 所依赖的比较器,否则反正默认的比较器(OrderComparator),然后调用 Listsort(Comparator c) 方法即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private static void sortPostProcessors (List<?> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {if (postProcessors.size() <= 1 ) {return ;null ;if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {if (comparatorToUse == null ) {
注册 同样是调用 AbstractBeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) 方法完成注册。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 private static void registerBeanPostProcessors ( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) {if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {else {for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
总结
BeanPostProcessor 的作用域是容器级别的,它只和所在的容器相关 ,当 BeanPostProcessor 完成注册后,它会应用于所有跟它在同一个容器内的 bean 。
BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext 对 BeanPostProcessor 的处理不同,ApplicationContext 会自动检测所有实现了 BeanPostProcessor 接口的 bean,并完成注册,但是使用 BeanFactory 容器时则需要手动调用 AbstractBeanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) 方法来完成注册
ApplicationContext 的 BeanPostProcessor 支持 Ordered,而 BeanFactory 的 BeanPostProcessor 是不支持的,原因在于ApplicationContext 会对 BeanPostProcessor 进行 Ordered 检测并完成排序,而 BeanFactory 中的 BeanPostProcessor 只跟注册的顺序有关。