spring统一资源加载策略
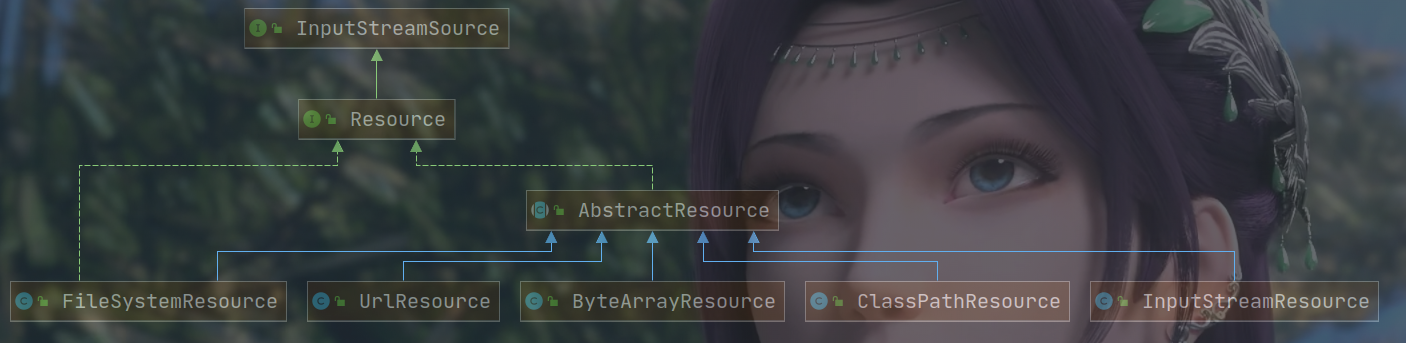
org.springframework.core.io.Resource 为 Spring 框架所有资源的抽象和访问接口,它继承 org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource接口。作为所有资源的统一抽象,Source 定义了一些通用的方法,由子类 AbstractResource 提供统一的默认实现。
统一资源:Resource org.springframework.core.io.Resource为Spring所有资源的抽象和访问接口,继承自org.springframework.core.io.InputStreamSource,Resource定义的统一方法由其子类AbstractResource提供默认实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {boolean exists () ;default boolean isReadable () {return true ;default boolean isOpen () {return false ;default boolean isFile () {return false ;getURL () throws IOException;getURI () throws IOException;getFile () throws IOException;default ReadableByteChannel readableChannel () throws IOException {return Channels.newChannel(getInputStream());long contentLength () throws IOException;long lastModified () throws IOException;createRelative (String relativePath) throws IOException;@Nullable getFilename () ;getDescription () ;
FileSystemResource:对 java.io.File 类型资源的封装,只要是跟 File 打交道的,基本上与 FileSystemResource 也可以打交道。支持文件和 URL 的形式,实现 WritableResource 接口。
ByteArrayResource:对字节数组提供的数据的封装。如果通过 InputStream 形式访问该类型的资源,该实现会根据字节数组的数据构造一个相应的 ByteArrayInputStream。
UrlResource:对 java.net.URL类型资源的封装。内部委派 URL 进行具体的资源操作。
ClassPathResource:class path 类型资源的实现。使用给定的 ClassLoader 或者给定的 Class 来加载资源。
InputStreamResource:将给定的 InputStream 作为一种资源的 Resource 的实现类。
AbstractResource 为 Resource 接口的默认实现,它实现了 Resource 接口的大部分的公共实现。
如果想要实现自定义的 Resource,记住不要实现 Resource 接口,而应该继承 AbstractResource 抽象类,然后根据当前的具体资源特性覆盖相应的方法即可。
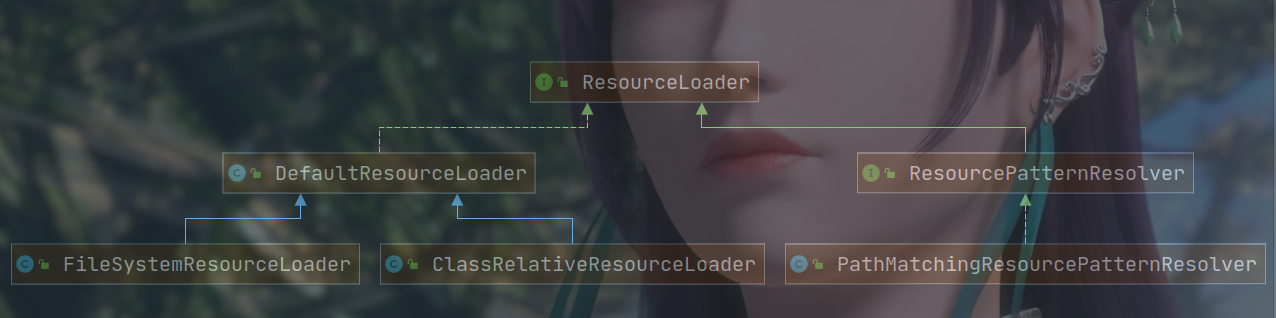
统一资源定位:ResourceLoader 定义 org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader 为 Spring 资源加载的统一抽象,具体的资源加载则由相应的实现类来完成,所以我们可以将 ResourceLoader 称作为统一资源定位器。
1 2 3 4 5 6 public interface ResourceLoader {String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;getResource (String var1) ;getClassLoader () ;
getResource根据所提供资源的路径 location 返回 Resource 实例,但是它不确保该 Resource 一定存在,需要调用 Resource.exist()方法判断。该方法的主要实现是在其子类 DefaultResourceLoader 中实现,支持以下模式的资源加载:
URL位置资源,如”file:C:/test.dat”。
ClassPath位置资源,如”classpath:test.dat”。
相对路径资源,如”WEB-INF/test.dat”,此时返回的Resource实例根据实现不同而不同。
getClassLoader 返回 ClassLoader 实例,对于想要获取 ResourceLoader 使用的 ClassLoader 用户来说,可以直接调用该方法来获取。
DefaultResourceLoader org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader 是 ResourceLoader 的默认实现。
构造函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public DefaultResourceLoader () {public DefaultResourceLoader (@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this .classLoader = classLoader;
当然,后续也可以使用setClassLoader进行设置。
1 2 3 public void setClassLoader (@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this .classLoader = classLoader;
getResource()方法 ResourceLoader 中最核心的方法为public Resource getResource(String location),DefaultResourceLoader提供了具体实现,他的两个子类并未覆盖此方法,所以ResourceLoader的资源加载策略就封装在 DefaultResourceLoader 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public Resource getResource (String location) {"Location must not be null" );for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : getProtocolResolvers()) {Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this );if (resource != null ) {return resource;if (location.startsWith("/" )) {return getResourceByPath(location);else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {return new ClassPathResource (location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());else {try {URL url = new URL (location);return (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) ? new FileUrlResource (url) : new UrlResource (url));catch (MalformedURLException ex) {return getResourceByPath(location);
首先,通过 ProtocolResolver 来加载资源,成功返回 Resource 。
否则,若 location 以 "/" 开头,则调用 #getResourceByPath() 方法,构造 ClassPathContextResource 类型资源并返回。代码如下:
1 2 3 protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path ) {new ClassPathContextResource(path , getClassLoader () );
再否则,若 location 以 "classpath:" 开头,则构造 ClassPathResource 类型资源并返回。在构造该资源时,通过 #getClassLoader() 获取当前的 ClassLoader。
再否则,构造 URL ,尝试通过它进行资源定位,若没有抛出 MalformedURLException 异常,则判断是否为 FileURL , 如果是则构造 FileUrlResource 类型的资源,否则构造 UrlResource 类型的资源。
最后,若在加载过程中抛出 MalformedURLException 异常,则委派 #getResourceByPath() 方法,实现资源定位加载。该过程和第二步 location 以 "/" 开头相同。
其子类可以通过重写getResourceByPath(String path)来返回和自身相关的资源类型 。
ProtocolResolver org.springframework.core.io.ProtocolResolver(是个函数式接口),用户自定义协议资源解决策略,如上介绍Resource所说:如果想要实现自定义的 Resource,应该继承 AbstractResource 抽象类,但是有了 ProtocolResolver 后,不需要直接继承 DefaultResourceLoader,改为实现 ProtocolResolver 接口也可以实现自定义的 ResourceLoader。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @FunctionalInterface public interface ProtocolResolver {@Nullable resolve (String location, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) ;
自定义的resolve添加到spring中:
1 2 3 4 5 public void addProtocolResolver (ProtocolResolver resolver) {"ProtocolResolver must not be null" );this .protocolResolvers.add(resolver);
FileSystemResourceLoader org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResourceLoader重写了getResourceByPath,使之从文件系统加载资源并以 FileSystemResource 类型返回:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 protected Resource getResourceByPath (String path) {if (path.startsWith("/" )) {1 );return new FileSystemContextResource (path);
FileSystemContextResource 为 FileSystemResourceLoader 的内部类,它继承 FileSystemResource 类,实现 ContextResource 接口。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 private static class FileSystemContextResource extends FileSystemResource implements ContextResource {public FileSystemContextResource (String path) {super (path);@Override public String getPathWithinContext () {return getPath();
ClassRelativeResourceLoader org.springframework.core.io.ClassRelativeResourceLoader是DefaultResourceLoader的另一个子类,和FileSystemResourceLoader一样,都是重新写了getResourceByPath()方法,然后有个内部类ClassRelativeContextResource。
ClassRelativeResourceLoader扩展的功能是可以根据给定的class所在包或者所在包的子包下加载资源。
ResourcePatternResolver ResourceLoader 的 Resource getResource(String location) 方法,每次只能根据 location 返回一个 Resource 。当需要加载多个资源时,我们除了多次调用 getResource(String location) 方法外,别无他法。org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver 是 ResourceLoader 的扩展,它支持根据指定的资源路径匹配模式每次返回多个 Resource 实例。
1 2 3 4 5 public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:" ;throws IOException;
ResourcePatternResolver在ResourceLoader的基础上增加了getResources方法:
1 2 throws IOException;
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是ResourcePatternResolver的子类,在父类的基础上额外还支持 Ant 风格的路径匹配模式(类似于 "/*.xml")。
构造函数 提供了三个构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher ();public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver () {this .resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader ();public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver (ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {"ResourceLoader must not be null" );this .resourceLoader = resourceLoader;public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver (@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {this .resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader (classLoader);
getResource 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public Resource getResource (String location) {return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader () {return this .resourceLoader;
该方法,直接委托给相应的 ResourceLoader 来实现。如果我们在实例化的 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 的时候,如果未指定 ResourceLoader 参数的情况下,那么在加载资源时,其实就是 DefaultResourceLoader 的过程。
getResources 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {"Location pattern must not be null" );if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);else {return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));else {int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:" ) ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/" ) + 1 :':' ) + 1 );if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);else {return new Resource [] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
非 "classpath*:" 开头,且路径不包含 通配符,直接委托给相应的 ResourceLoader 来实现。其他情况,调用 #findAllClassPathResources(...)、或 #findPathMatchingResources(...) 方法,返回多个 Resource 。
findAllClassPathResources 当 locationPattern 以 "classpath*:" 开头但是不包含通配符,则调用 findAllClassPathResources(...) 方法加载资源。该方法返回 classes 路径下和所有 jar 包中的所有相匹配的资源。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {String path = location;if (path.startsWith("/" )) {1 );if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {"Resolved classpath location [" + location + "] to resources " + result);return result.toArray(new Resource [0 ]);
真正执行加载的是在 doFindAllClassPathResources(...) 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 protected Set<Resource> doFindAllClassPathResources (String path) throws IOException {new LinkedHashSet <>(16 );ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();if (!StringUtils.hasLength(path)) {return result;
<1>处根据 ClassLoader 加载路径下的所有资源。在加载资源过程时,如果在构造 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 实例的时候如果传入了 ClassLoader,则调用该 ClassLoader 的 getResources() 方法,否则调用 ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path) 方法。另外,ClassLoader.getResources() 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public Enumeration<URL> getResources (String name) throws IOException {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") new Enumeration <?>[2 ];if (parent != null ) {0 ] = parent.getResources(name);else {0 ] = BootLoader.findResources(name);1 ] = findResources(name);return new CompoundEnumeration <>(tmp);
如果当前父类加载器不为 null ,则通过父类向上迭代获取资源,否则调用BootLoader.findResources(name);
<2> 处,遍历 URL 集合,调用 convertClassLoaderURL(URL url) 方法,将 URL 转换成 UrlResource 对象。
1 2 3 protected Resource convertClassLoaderURL (URL url) {return new UrlResource (url);
<3> 处,若 path 为空(“”)时,则调用 addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(...)方法。该方法主要是加载路径下得所有 jar 包。
由上可以看出,#findAllClassPathResources(...) 方法,其实就是利用 ClassLoader 来加载指定路径下的资源,不论它是在 class 路径下还是在 jar 包中。如果我们传入的路径为空或者 /,则会调用 addAllClassLoaderJarRoots(...) 方法,加载所有的 jar 包。
findPathMatchingResources 当 locationPattern 中包含了通配符 ,则调用该方法进行资源加载。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());new LinkedHashSet <>(16 );for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {URL rootDirUrl = rootDirResource.getURL();if (equinoxResolveMethod != null && rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle" )) {URL resolvedUrl = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null , rootDirUrl);if (resolvedUrl != null ) {new UrlResource (rootDirUrl);if (rootDirUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirUrl) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {else {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {"Resolved location pattern [" + locationPattern + "] to resources " + result);return result.toArray(new Resource [0 ]);
确定目录,获取该目录下得所有资源。
在所获得的所有资源后,进行迭代匹配获取我们想要的资源。
在这个方法里面,我们要关注两个方法,一个是 #determineRootDir(String location) 方法,一个是 doFindPathMatchingXXXResources(...) 等方法。
determineRootDir(String location) 方法,主要是用于确定根路径。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 protected String determineRootDir (String location) {int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(':' ) + 1 ;int rootDirEnd = location.length();while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {'/' , rootDirEnd - 2 ) + 1 ;if (rootDirEnd == 0 ) {return location.substring(0 , rootDirEnd);
例:
原路径
确定根路径
classpath*:test/cc*/spring-*.xml
classpath*:test/
classpath*:test/aa/spring-*.xml
classpath*:test/aa/
总结 Spring资源加载过程如下:
Spring 提供了 Resource 和 ResourceLoader 来统一抽象整个资源及其定位。使得资源与资源的定位有了一个更加清晰的界限,并且提供了合适的 Default 类,使得自定义实现更加方便和清晰。
AbstractResource 为 Resource 的默认抽象实现,它对 Resource 接口做了一个统一的实现,子类继承该类后只需要覆盖相应的方法即可,同时对于自定义的 Resource 我们也是继承该类。
DefaultResourceLoader 同样也是 ResourceLoader 的默认实现,在自定 ResourceLoader 的时候我们除了可以继承该类外还可以实现 ProtocolResolver 接口来实现自定资源加载协议。
DefaultResourceLoader 每次只能返回单一的资源,所以 Spring 针对这个提供了另外一个接口 ResourcePatternResolver ,该接口提供了根据指定的 locationPattern 返回多个资源的策略。其子类 PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver 是一个集大成者的 ResourceLoader ,因为它即实现了 Resource getResource(String location) 方法,也实现了 Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) 方法。